SBOM as a Global Initiative
SBOMs are no longer viewed as a best practice; they are now essential for OEMs to maintain software supply chain integrity and ensure compliance with cybersecurity regulations, such as UN R155, ISO/SAE 21434, and Auto-ISAC Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) guidance.
Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) is developing a comprehensive SBOM framework to improve visibility across the software supply chain. This framework will complement other international SBOM initiatives and frameworks.
For Japanese automakers, implementing comprehensive SBOM management isn’t just about compliance – it’s a competitive differentiator, enabling them to secure more global contracts with OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers that now require verifiable software traceability, immediate vulnerability identification, and ongoing compliance assurance across heavily regulated international markets.
This article will highlight the significant benefits for Japanese OEMs to produce SBOMs.
The SBOM Value Proposition for Japanese OEMs
SBOMs benefit Japanese OEMs and automotive trade suppliers in several ways:
OSSRA reports that 33% of current automotive codebases contain high-risk vulnerabilities, primarily due to outdated or unmaintained open-source components.
Enhanced software supply chain transparency: An SBOM can map every open-source relationship and version history within a vehicle’s software stack, enabling OEMs and international suppliers to identify and mitigate vulnerable dependencies earlier and faster in the production lifecycle. This level of transparency is essential when assessing third-party components for security risks, detecting malicious packages, validating software integrity across ECUs, and ensuring that all components comply with international cybersecurity regulations and industry standards.
Hikari Seiko, a Japanese precision parts manufacturer, had over 500 GB of sensitive data (333,000 files) exfiltrated by the Qilin ransomware group in February 2025.
Risk management: SBOMs are critical for protecting interconnected software-defined vehicle (SDV) components from insecure OTA updates, impacted sensors, and other ECU-related exploits by providing full visibility into all software dependencies, tracking and publishing version updates, and supplier name attributes. SBOMs enhance threat modeling programs and ensure that every vehicle component, from infotainment systems to ADAS and telematics modules, is accounted for and documented.
Improved supplier collaboration: An SBOM can increase trust and provide more substantial procurement confidence through provenance and license visibility on the sales and partnerships side. Many vendors require OEMs to supply an accurate and up-to-date SBOM before contract negotiations. OEMs can evaluate the vendors’ risk management and maturity and assess the security posture of their software components. Regulatory concerns are further addressed by reviewing dependency trees and component versions to ensure full accountability across the supply chain.
When SBOM Automation Becomes Essential for Vehicle Development
SBOMs are also integral for strengthening DevSecOps pipelines by integrating into CI/CD workflows to detect outdated third-party components and validate the integrity of builds before deployment. Running a quick SBOM analysis can show which libraries and dependencies have high-risk vulnerabilities that require immediate attention.
DevSecOps teams can review all findings and prioritize mitigation strategies accordingly, such as patching critical OS updates, implementing automated testing for security regressions, and enforcing code policies that restrict the use of deprecated components.
This process helps improve Japanese OEMs’ ability to shorten development cycles through historical version tracking and automated dependency analysis. Product security teams also benefit by reducing the time and effort required to identify and remediate vulnerable components later in the SDLC. This can significantly delay production and require re-engineering of ECUs or other telematics systems before they can be shipped.
Japanese OEMs can leverage machine-processable and compliance-ready SBOM formats like CycloneDX and SPDX to automate software component tracking, vulnerability detection, and license compliance across their connected vehicle software ecosystem. SBOMs also help OEMs reduce costs through automated triage and regulatory auditing approval processes.
Benefits for the Japanese Automotive Ecosystem
Additional incentives exist for Japanese OEMs to produce SBOMs, which have a positive ripple effect across the entire automotive ecosystem.
Producers: Halting production to fix a critical supply chain vulnerability in an outdated open-source package or defective sensor controller isn’t feasible. SBOMs provide OEMs with faster mitigation by identifying vulnerable components earlier in the development lifecycle, better tracking of all software dependencies, vehicle parts, and complete license clarity to avoid any open-source and third-party risks that can literally derail production timelines.
Procurement: Cybersecurity is a core consideration during procurement processes. SBOMs remove the guesswork for procurement teams, which can accelerate vendor assessment, streamline contract negotiations, and ultimately reduce logistics costs. SBOMs provide clear, verifiable documentation that helps OEMs better source and qualify suppliers, improve quality control, and build better relationships across the international automotive ecosystem to secure new vendor agreements and tenders.
Regulators/Governments: Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) recently published a comprehensive SBOM implementation guide to strengthen collaboration between government agencies and the privately controlled automotive sector. The initiative aims to enhance software supply chain transparency and align Japan’s cybersecurity posture with other international standards, such as the EU Cyber Resilience Act and the CISA/NSA global SBOM initiative.
The move also gives Japanese automakers a competitive edge in the U.S. market, as tariffs on Japanese imported vehicles have been reduced from 27.5% to 15% under a recent executive order signed by President Trump. An SBOM further strengthens this advantage by providing verifiable proof of software provenance and cybersecurity compliance.
C2A Security: Automating SBOMs for Japanese Supply Chains
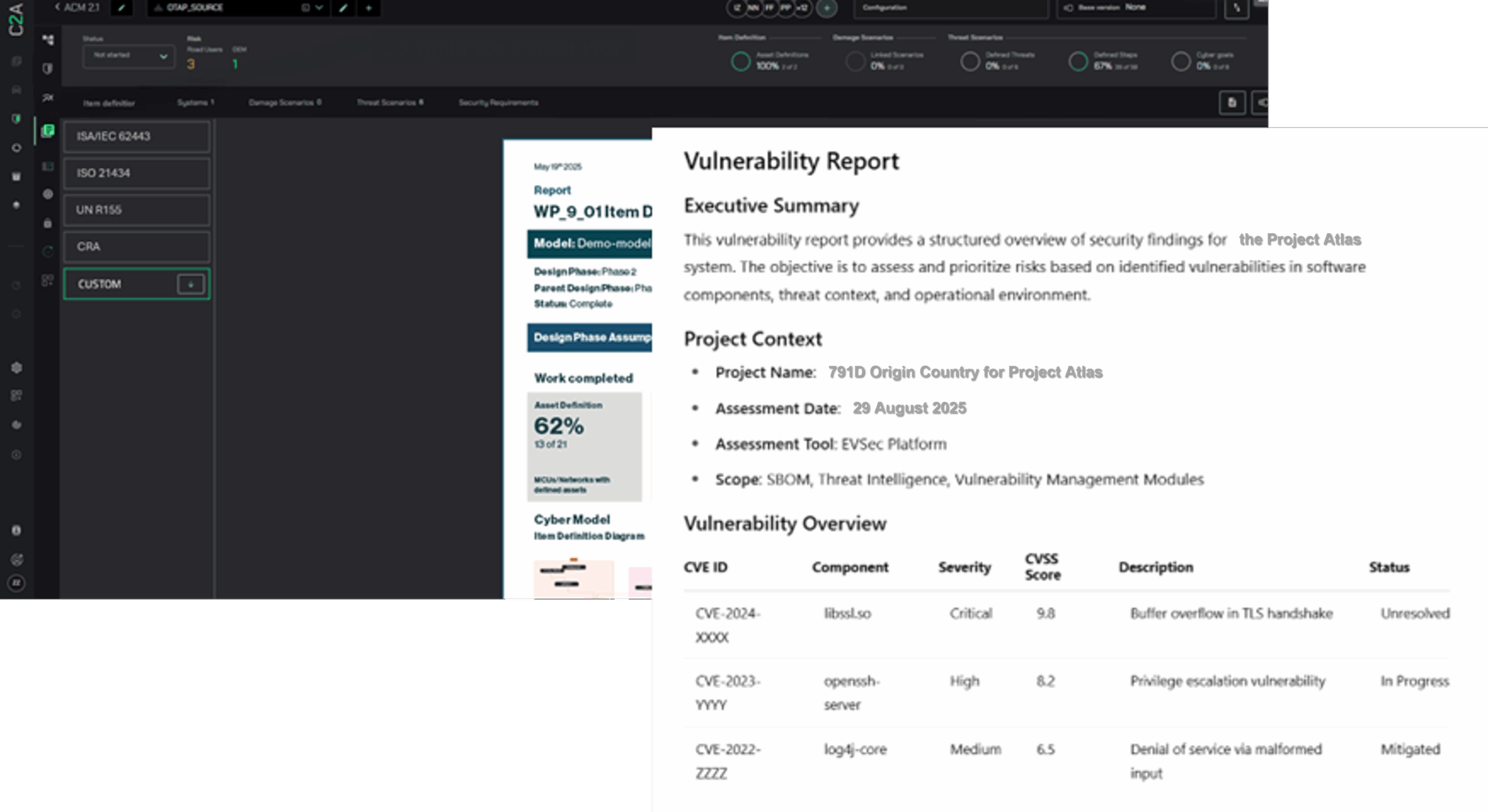
C2A Security, aligned with global regulatory frameworks, empowers Japanese OEMs with automated SBOM/HBOM ingestion, vulnerability analysis, and context-driven triage.
EVSec, our compliance accelerator, links SBOMs directly to standards such as FDA 524B, EU CRA, NIS2, and RED – turning compliance from a manual burden into an automated workflow.
EVSec enables:
- Automated ingestion and mapping of SBOM/HBOM to vulnerabilities
- VEX generation and ISO/SAE 21434 compliance reporting with each version
- Context-based risk prioritization for faster decision-making
- Regulatory and procurement reporting at the push of a button
Real-World Trust in Action
“We wanted to bring secure, advanced connected services to the market faster. Therefore, we needed to work with external professionals. Accenture’s expertise and drive, which were with us each step from process design to TARA execution, plus C2A Security’s solution, enabled us to achieve TARA of consistent quality in a short period of time.”
— Hideaki Inoue, Assistant General Manager, Mobility Business Division, Mitsubishi Motors Corporation
Schedule a demo to learn how C2A Security can help Japanese OEMs enhance transparency, reduce compliance friction, and build vendor trust across global supply chains.